 February 27, 2019 6:01 am |
February 27, 2019 6:01 am |
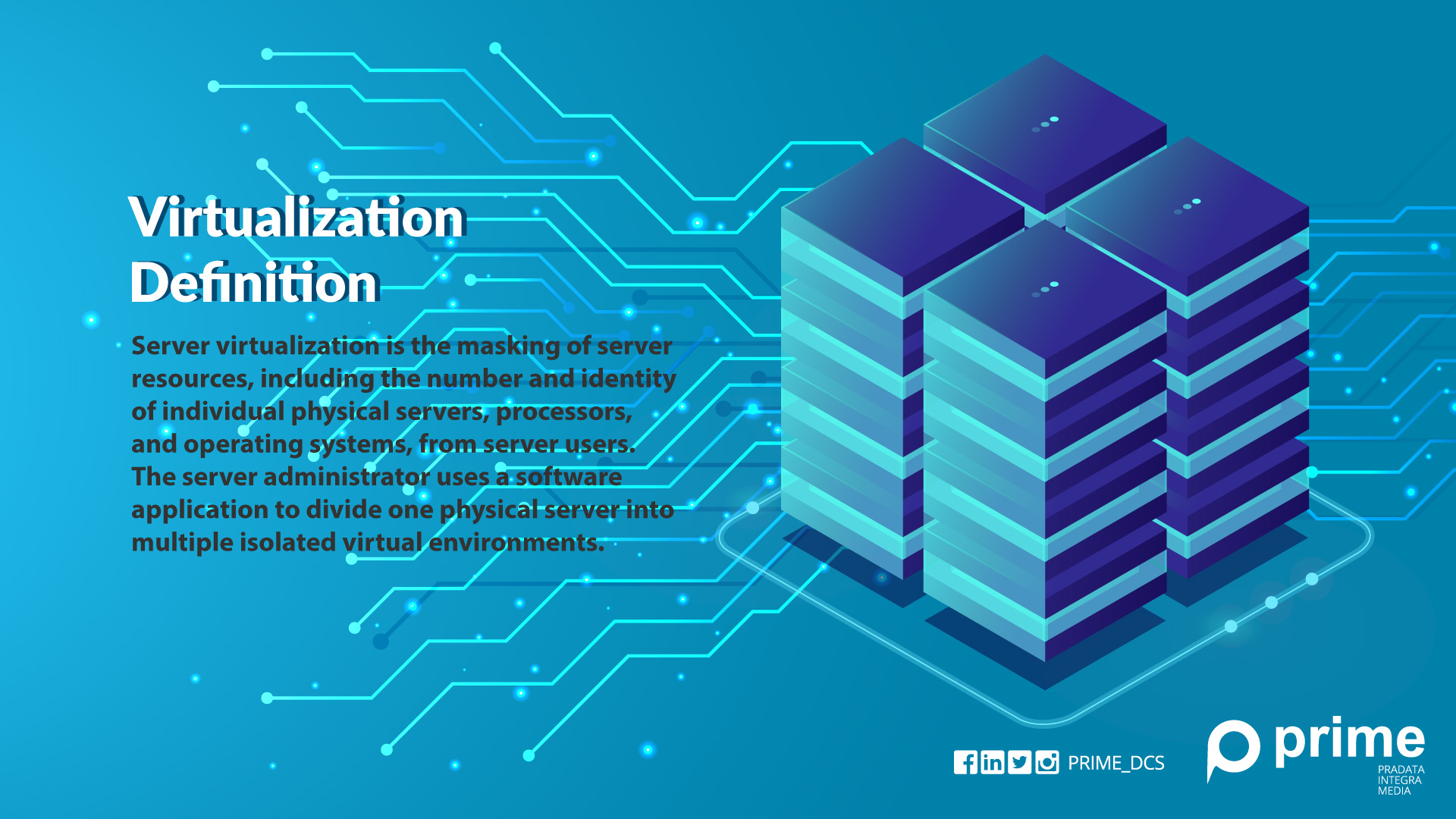
What Is Virtualization?
Virtualization enables you to share hardware so that you can use multiple operating systems (guest operating systems). Virtualization can make a large single storage area into several smaller storage places.
Hypervisor as the code of the computer connected to the hardware. This makes you able to separate one system into a separate, different, and safe environment called a virtual machine / virtual machine (VM). This VM emphasizes the ability of the hypervisor to manage the resources of the hardware and is properly supported. Virtualization helps you get value from your device investment.
Physical hardware, which is equipped with a hypervisor, is called a host, while many VMs that use their resources are guests. Guests use computing resources, such as mainframes, memory, and storage. The resource is a collection of movable resources. Operators will manage different virtual mainframes, memory, storage, and resources. Because receiving guests who receive resources will like them after they need it.
How Virtualization Works
Hypervisors, as software, share physical resources from the virtual environment for things that these resources need. The way most companies do virtualization with a hypervisor is used in operating systems (such as laptops) or installed directly on hardware (as a server). In order for the virtual environment to be used, Hypervisors take their physical resources and share them.
Resources are partitioned according to the needs of the physical environment to many virtual environments. Users interact and execute calculations in a virtual environment, usually called a guest machine or virtual machine. Virtual machine functions as a single data file. And like other digital files, it can be moved from one computer to another. When opened on one computer, the file is expected to function the same.
When a virtual environment is running and the user or program issues instructions that require additional resources from the physical environment, the hypervisor delivers requests to the physical system and stores changes. Everything happens at speeds approaching the original speed, especially if the request is sent via an open source hypervisor based on KVM, the Kernel-based Virtual Machine.
Computer Equipment That Can Be Virtualized
The following are some computer equipment that can be virtualized, including:
- Server virtualization
From the perspective of access and management, a physical server can be multiple servers. This is called a virtual server or virtual machine (VM).
- Desktop Virtualization
Similar to server virtualization, desktop virtualization can double. First, users can run several desktop operating systems (Apple Mac OS and Microsoft Windows OS) on the same computer. Second, virtualization makes data and services that are owned by users placed on computers along with data and services that are used by others.
- Storage virtualization
One physical storage can be several virtual drivers. That is, by using separate windows on a common management console, IT administrators can treat virtual drives like physical drives.
- Application Virtualization
When doing virtualization, applications written for an operating system environment can be run in other operating environments to improve application compatibility and ease of management. The operation will be directed to the appropriate operating system.
- Network Virtualization
To create a virtual router on a network, several IP addresses can be supported by a physical router. To make a virtual switch on physical Ethernet the same so that it can support multiple MAC addresses (media access control). A physical hardware can be partitioned into several virtual routers or switches to save costs.
Purpose of Virtualization
Companies have goals in virtualization, namely high-level performance, availability, reliability, agility, or to create a basis for integrated security and management. In addition to this, there are many other goals to be achieved from a company, including:
- Access applications through the network of all network-connected devices, even for applications that are not designed to work on the device.
- Improve security and ease of environmental management by isolating workloads or applications with one another.
- Make the application work even though it is designed for operating systems of different types by isolating applications from the operating system.
- Make an application work on a foreign operating system by isolating the application from the operating system.
- Provide access to operate applications from different machines simultaneously so that the number of people that can be supported by the application increases.
- Reducing the time needed to run the application, by separating the data or application itself and spreading work on several systems
- Optimizing utilization with a single system
- Increase the reliability or availability of the application or workload with repetition
Virtualization has grown rapidly from specialized technology to core technology in IT infrastructure. IT solution companies offer many types of choices and goals for virtualization. Each is designed to provide solutions to different business problems.
Tags: application virtualization, desktop virtualization, how virtualization works, hypervisor, IT solution, network virtualization, server virtualization, storage virtualization, virtual machine, virtualization, what is virtualization